How To Install Microsoft Security Patches
Magento'southward about empowering characteristic is its open up source architecture. It allows developers to freely configure the platform and create complex custom solutions for ecommerce. Still, open architecture has an unfortunate security vulnerability, which makes the platform subject to hacker attacks. Another reason why Magento is and so prone to security attacks lies in its popularity. For today, more 250,000 online stores around the world are powered past Magento.
Table of contents:
Why do you need Magento 2 security patches?
Listing of Magento 2 security patches
How to install Magento security patches
How to check Magento store security
Why exercise you need Magento two security patches?
In the first Magento versions, the development policy was more focused on improving the platform and calculation new features. This meant that security issues were mostly disregarded, and to get rid of a certain security vulnerability, a store owner would accept to merely update their Magento to the latest version.
In 2022, the Magento squad decided to accost the security with more than attention, and since then Magento security patches have been released regularly. Even though this determination did not entirely resolve the general upshot of security, it massively improved the security status and prevented a number of hacker attacks.
So, what are security patches in Magento 2? A security patch is a modify of code that fixes a certain vulnerability. The fixes are supplied in the form of a cocky-installing patch script, which locates the identify where the code fix belongs to, automatically applies the update to it and saves the effect. Keep in mind that security patches rely on core code files for proper installation, which means that if yous alter core code, there is a chance the patches volition fail to install.
But are the outcomes of ignoring security patches that severe? Here are the 4 most common consequences of a Magento store beingness hacked :
- Credit menu information of the customers can go stolen. In fact, certain Magento integrations and extensions, especially payment ones, are from fourth dimension to time discovered to be attacked and abused by fraudulent hacker groups. The contempo case concerned PayPal integration Payflow Pro, it was hacked and utilized for stealing debit and credit card numbers.
- Ransomware can get installed into your webstore. Ransomware is the type of malicious software that encrypts your code and denies you admission to it until yous pay for its release.
- Webstore server can get compromised past hackers. Information technology means that it can be used for illicit activities, in item, for sending spam emails.
- Malware can become installed into your store, farther spreading and affecting your visitors. Equally a event, your website gets blocked by search engines until the security is restored, which results in profit loss and sure reputation impairment. In astringent cases, y'all will cease upwardly losing critical customer data.
With all that in mind, allow us motion to the latest Magento ii security patches and their clarification.

Partner With Us
Let'southward discuss how to grow your business organisation. Get a Costless Quote.
Talk to Andrey
Listing of Magento 2 security patches
This is the list of the most disquisitional Magento security patches released over the last year:
| Patch Title | Clarification | Versions stock-still in |
| APPSEC-1281: Remote Code Execution if the configuration setting allowing symlinks is enabled | AllowSymlinks option from the configuration settings allowed to upload an image containing malicious code. | CE i.9.iii.iii, EE 1.14.3.three |
| APPSEC-1777: Remote Code Execution in DataFlow | DataFlow functionality utilized for uploading and executing arbitrary lawmaking. | CE 1.ix.three.iii, EE 1.xiv.three.3 |
| APPSEC-1686: Remote Code Execution in the Admin console | Admission to store CMS allowed to remotely execute code. | CE ane.9.3.3, EE one.fourteen.3.three, Magento 2.0.14 and Magento 2.1.7 |
| APPSEC-1320: SQL injection in Visual Merchandiser (Enterprise Edition) | SQL injection vulnerability in the Visual Merchandiser enabled a user with admin condition to edit the database | EE ane.fourteen.three.3 |
| APPSEC-1634: XSS in information fields | Inability to filter information in certain admin tables immune for cross-site scripting attacks. | CE one.9.3.3, EE 1.14.3.three |
| APPSEC-1759: XSS in Admin panel configuration | A person with the admin role tin enter a malicious code that affects other admin panel pages. | CE one.nine.3.3, EE one.14.3.3 |
| APPSEC-1549: CSRF later logout – form key not invalidated | Grade key failed to invalidate on logout, allowing i to execute malicious commands later the admin logs out. | CE 1.ix.iii.three, EE 1.xiv.3.3 |
| APPSEC-1626: RCE in video upload | Video upload functionality allowed to upload malicious PHP files. | CE and EE 2.0.14/2.1.7 |
| APPSEC-1746: Zend Mail vulnerability – continued | Zend Mail vulnerability was fixed in ii.0.12/ii.1.4 version, just was discovered to used to avoiding the implemented protection. | CE and EE ii.0.xiv/2.1.7 |
| APPSEC-1559: Possible remote code execution in e-mail reminders | Electronic mail reminder functionality enabled objects instantiation. | CE and EE 2.0.fourteen/ii.1.vii |
| APPSEC-1752: Stored XSS in admin console | User data logged into admin panel was not escaped properly, allowing lower level admins attack other administrators. | CE and EE 2.0.fourteen/2.1.vii |
| APPSEC-1699: API tokens not invalidated later on disabling admin user | API tokens were not invalidated afterward the admin user disabling, allowing for attacks or unauthorized actions. | CE and EE 2.0.14/2.1.vii |
| APPSEC-1632: Password shown in action log (EE only) | Under certain atmospheric condition, the ambassador password was shown in plainly text in the action log. | EE 2.0.xiv/two.1.vii |
| APPSEC-1663: Mass actions exercise not follow ACL | Low-level admins were able to perform unauthorized actions. | CE and EE 2.0.14/ii.1.7 |
| APPSEC-1661: UI controllers do not follow ACL | Low-level admins were able to extract the information they were non authorized to admission. | CE and EE 2.0.14/2.1.7 |
| APPSEC-1679: APIs vulnerable to CSRF | Some customer authenticated APIs were vulnerable to CSRF and phishing attacks. | CE and EE 2.0.fourteen/2.1.7 |
| APPSEC-1610: Custom admin path disclosure | Payments module disclosed custom admin path location, allowing for password guessing or other hacks. | CE and EE ii.0.14/2.1.7 |
| APPSEC-1666: Data leak | Requests returned past AJAX calls contained exposing configuration info. | CE and EE 2.0.14/2.ane.7 |
| APPSEC-1800: Remote Code Execution vulnerability in CMS and layouts | While creating a new CMS page, a depression-level admin could introduce malicious code. | Magento Open Source ane.9.three.6, Magento Commerce 1.fourteen.3.6, Magento 2.0.xvi, Magento 2.ane.9 |
| APPSEC-1887: Capricious File Disclose | Theme creation vulnerability, assuasive to disclose or delete Magento installation arrangement files. | Magento ii.0.xvi, Magento 2.one.9 |
| APPSEC-1850: Capricious File Delete | The File Delete module could be used to upload and delete arbitrary files. | Magento ii.0.16, Magento 2.ane.9 |
| APPSEC-1851: Arbitrary file delete + Lack of input sanitization leading to Remote Code Execution | Depression-level Magento admin could make use of functional test vulnerability and get full remote lawmaking execution. | Magento 2.0.16, Magento 2.i.9 |
| APPSEC-1567: Order history disclosure | Generic society info enabled hackers to obtain full order information. | Magento 2.0.16, Magento two.ane.nine |
| APPSEC-1769: Overwrite a Relative Path in Sitemap | Sitemap generation tool could be utilized for sensitive files overwrite. | Magento ii.0.sixteen, Magento ii.1.ix |
| APPSEC-1713: Setup pages betrayal sensitive data | Sensitive URL info leak, including controller location. | Magento 2.0.16, Magento 2.i.ix |
| APPSEC-1852: CSRF + Stored Cross Site Scripting (customer grouping) | A customer group vulnerability used to create a URL for CSRF attack. | Magento Open Source 1.ix.three.half-dozen, Magento Commerce one.14.3.6, Magento 2.0.sixteen, Magento two.i.9 |
| APPSEC-1482: Security Issue with referrer | A URL can be added to Magento site, redirecting users to malicious websites. | Magento 2.0.16, Magento 2.1.nine |
| APPSEC-1502: Stored XSS – Add new group in Aspect set up name | Malicious code could be injected into custom product attributes. | Magento 2.0.16, Magento two.1.9 |
| APPSEC-1494: AdminNotification Stored XSS | Network Man-in-the-eye attack could inject code on the Magento Admin RSS feed. | Magento Open Source 1.9.3.6, Magento Commerce i.fourteen.iii.half-dozen, Magento ii.0.16, Magento 2.ane.nine |
| APPSEC-1793: Potential file uploads solely protected by .htaccess | The non-Apache installation independent executable scripting uploads that tin be used for malicious purposes. | Magento Open Source 1.9.3.half dozen, Magento Commerce i.14.3.6, Magento 2.0.16, Magento 2.1.9 |
| APPSEC-1819: Customer login authenticates ii dissimilar sessions | Incorrect setup of an expired user session, which tin exist used by a hacker for access. | Magento 2.0.16, Magento 2.1.ix |
| APPSEC-1802: Client registration through frontend does not have anti-CSRF protection | CSRF protection to the customer registration process, preventing from taking over accounts. | Magento 2.0.sixteen, Magento 2.1.9 |
| APPSEC-1493: CMS Folio Title Stored XSS | Executable scripts can exist injected into non-executable areas, such as page title. | Magento 2.0.16, Magento 2.ane.ix |
| APPSEC-1755: Anti-CSRF form_key is not changed after login | Anti-CSRF tokens did non alter properly afterward the user logged in. | Magento ii.0.xvi, Magento ii.ane.9 |
| APPSEC-1853: CSRF + Stored Cross Site Scripting in newsletter template | Vulnerability in newsletter templates allowed for URL cosmos that can be farther exploited for a CSRF assail. | Magento Open Source one.nine.3.six, Magento Commerce 1.xiv.iii.six, Magento 2.0.16, Magento 2.1.nine |
| APPSEC-1729: XSS in admin order view using order condition label in Magento | The code tin can be injected into sales gild records, resulting in an XSS attack. | Magento Open Source 1.ix.3.6, Magento Commerce 1.14.3.6, Magento 2.0.16, Magento 2.ane.ix |
| APPSEC-1775: Stored Cantankerous-Site Scripting in electronic mail template bypass | Malicious code tin can be inserted into email templates. | Magento 2.0.16, Magento 2.one.ix |
| APPSEC-1591: Stored XSS on product thumbnail | Products containing malicious code in the thumbnail can be added by Magento admin. | Magento two.0.16, Magento 2.1.nine |
| APPSEC-1896: Possible XSS in admin order view using social club lawmaking label | Malicious code can be injected in the Society view. | Magento two.0.xvi, Magento 2.1.9 |
| APPSEC-1673: Stored xss using svg images in Favicon | SVG production images could contain malicious code. | Magento two.0.16, Magento 2.1.ix |
| APPSEC-1773: Injection on Page leading to DoS | While new folio creation, the page counter can be modified, resulting in an integer overflow. | Magento 2.0.16, Magento two.one.9 |
| APPSEC-1577: Stored XSS in integration activation | Malicious code could be injected in the integration activation. | Magento two.0.xvi, Magento 2.1.9 |
| APPSEC-1510: Whatsoever admin user tin upload Favicon Icon | Low-level admin could modify a favicon image for the unabridged website. | Magento 2.0.16, Magento ii.i.9 |
| APPSEC-1545: Stored XSS through customer group name in admin panel | Customer fields can exist injected with scriptable code, resulting in an XSS assault. | Magento 2.0.16, Magento 2.1.9 |
| APPSEC-1535: Access Control Lists not validated when using quick edit style in tables | Access Control Lists were not properly checked. | Magento 2.0.xvi, Magento 2.1.9 |
| APPSEC-1588: Guild Item Custom Pick Disclosure | Information virtually past orders can be retrieved during checkout. | Magento Open up Source 1.ix.3.6, Magento Commerce 1.fourteen.3.6, Magento 2.0.sixteen, Magento 2.1.9 |
| APPSEC-1701: API token does not correctly expire | Due to incorrect expiration of customer and admin tokens, cookies tin be reused for criminal purposes. | Magento ii.0.xvi, Magento ii.one.9 |
| APPSEC-1630: Anonymous users tin can view upgrade progress updates | An bearding user could cheque Magento upgrade status by visiting an internal URL. | Magento 2.0.xvi, Magento 2.1.ix |
| APPSEC-1628: Full Path Disclosure Spider web Root Directory | Magento installation system path was disclosed. | Magento 2.0.sixteen, Magento 2.ane.ix |
| APPSEC-1599: Admin login does not handle autocomplete characteristic correctly | Incorrect autocomplete in the admin panel that could issue in information leak. | Magento Open up Source 1.ix.3.half-dozen, Magento Commerce 1.xiv.iii.vi, Magento 2.0.16, Magento ii.1.9 |
| APPSEC-1709: Customer e-mail enumeration through frontend login | Contact emails were leaked by the account lockout mechanism. | Magento 2.0.16, Magento 2.1.9 |
| APPSEC-1495: Any user can interact with the sales guild part despite not being authorized | A logged-in user could modify order fields. | Magento Open Source one.ix.3.vi, Magento Commerce ane.14.3.half-dozen, Magento 2.0.16, Magento ii.1.nine |
| APPSEC-2001: Authenticated Remote Code Execution (RCE) using custom layout XML | Custom layout XML tin be used to copy whatsoever file. | Magento Open Source one.9.three.9, Magento Commerce 1.14.3.ix |
| APPSEC-2015: Authenticated Remote Code Execution (RCE) through the Create New Society characteristic (Commerce only) | Gift carte du jour functionality tin can be used to inject a malicious string | Magento Open Source 1.9.iii.9, Magento Commerce one.14.3.nine |
| APPSEC-2042: PHP Object Injection and RCE in the Magento admin panel (Commerce Target Dominion module) | An administrator could create dominion-based production relations that tin trigger remote code execution. | Magento Open Source ane.9.iii.9, Magento Commerce i.xiv.3.9 |
| APPSEC-2029: PHP Object Injection and Remote Lawmaking Execution (RCE) in the Admin panel (Commerce) | With admission to Commerce Target dominion module, an ambassador could create rule-based product relations that tin can trigger remote code execution. | Magento Open Source 1.9.3.9, Magento Commerce 1.14.3.9 |
| APPSEC-2007: Authenticated SQL Injection when saving a category | Through request data manipulation, a malicious string can be inserted into the database, triggering the SQL injection. | Magento Open Source 1.9.3.ix, Magento Commerce 1.14.three.9 |
| APPSEC-2027: CSRF is possible against Web sites, Stores, and Store Views | CSRF vulnerabilities allow to delete websites, stores or store views. | Magento Open Source i.nine.three.9, Magento Commerce ane.xiv.3.9, Magento two.ane.14, Magento 2.2.v |
| APPSEC-1882: The cron.php file can leak database credentials | Database credentials could be leaked if information technology was non possible to plant connection to the database. | Magento Open Source 1.nine.3.9, Magento Commerce 1.14.three.9 |
| APPSEC-2014: Authenticated Remote Code Execution (RCE) through the Magento admin panel (swatches module) | Remote control over code execution could exist achieved via swatches module vulnerability. | Magento 2.1.14 |
| APPSEC-2054: Remote Code Execution (RCE) via product import | A person with admin rights could add malicious code to the server. | Magento 2.1.14, Magento 2.ii.5 |
| APPSEC-2042: PHP Object Injection and RCE in the Magento 2 EE admin console (Commerce Target Dominion module) | PHP Object Injection and RCE in the Magento 2 EE admin console (Commerce Target Rule module) | Magento ii.1.14, Magento Open Source i.9.3.9, Magento Commerce 1.14.three.ix |
| APPSEC-2055: PHP Object Injection and RCE in the Magento 2 Commerce admin console (Schedule Import/Export Configuration) | An admin who had access to import/export logic could insert malicious data used for PHP object injection and Remote Lawmaking Execution. | Magento 2.ane.14 |
| APPSEC-2048: SQL Injection through API | An API user could, via API endpoints, perform SQL Injection | Magento two.1.14, Magento ii.ii.5 |
| APPSEC-2025: Arbitrary File Delete via Production Image | Admin could send modified information to the WYSIWYG admin component and delete capricious files. | Magento 2.one.14, Magento ii.two.five |
| APPSEC-1838: RSS session admin cookie can be used to proceeds Magento administrator privileges. | Access to Magento Admin Portal could be gained via low privilege RSS session cookie. | Magento Open Source 1.9.iii.six, Magento Commerce 1.xiv.three.half-dozen |
| APPSEC-1835: Exposure of Magento secret cardinal from app/etc/local.xml | Admin could create content that would expose sensitive Magento installation information. | Magento Open Source 1.9.3.6, Magento Commerce 1.fourteen.three.6 |
| APPSEC-1861: PHP Object Injection in product entries leading to Remote Lawmaking Execution | Malicious code could be injected into promo fields. | Magento Open up Source one.nine.3.seven, Magento Commerce 1.14.three.7, Magento 2.0.17, Magento 2.1.10, Magento 2.ii.1 |
| APPSEC-1830: PHP Object Injection in product attributes leading to Remote Code Execution | Injectable cookie could be inserted in the production attributes. | Magento Open up Source i.9.3.7, Magento Commerce 1.14.3.vii, Magento 2.0.17, Magento ii.one.10, Magento 2.two.1 |
| APPSEC-1893: PHP Object Injection in product metadata leading to Remote Code Execution | The injectable code could be inserted in the swatches feature. | Magento 2.0.17, Magento 2.one.10, Magento two.two.i |
| APPSEC-1915: Remote Code Execution in CMS Page Area | Admin could create a CMS folio that would be parsed incorrectly, resulting in remote code execution. | Magento Open up Source one.9.three.7, Magento Commerce ane.xiv.3.7 |
| APPSEC-1830: PHP Object Injection in product attributes leading to Remote Code Execution | 1 tin can create a widget block with malicious code. | Magento Open up Source i.9.3.seven, Magento Commerce 1.14.three.seven, Magento 2.0.17, Magento two.one.10, Magento ii.ii.1 |
| APPSEC-1932: Remote Code Execution Using XML Injection | Injectable XML could be inserted into the layout table, giving an opportunity to remote lawmaking injection. | Magento Open up Source 1.9.3.8, Magento Commerce one.14.iii.8 |
| APPSEC-1938: Remote Code Execution – additional ready not included in SUPEE-9652 | Information can be inserted into a return path leading to Remote Code Execution (RCE). | Magento Open Source 1.nine.three.8, Magento Commerce 1.14.3.8 |
| APPSEC-1964: Remote Lawmaking Execution by (semi-)arbitrary file deletion for admin users with admission to Import | An XML file could be imported, giving an opportunity to Remote Code Execution (RCE). | Magento Open Source 1.9.3.eight, Magento Commerce 1.14.iii.8 |
| APPSEC-1951: JavaScript execution in the administrator panel | Ane could insert a script to the storefront field, leading to JavaScript code execution. | Magento 2.0.18, Magento two.ane.12, Magento two.two.3 |
| APPSEC-1952: Remote Code Execution using media upload | Using a path traversal vulnerability, one could remotely execute code during the media upload process. | Magento 2.0.18, Magento ii.1.12, Magento 2.2.3 |
| PRODSECBUG-2122: PHP Object Injection (POI) and Remote Lawmaking Execution (RCE) in the Magento 2.1.xv Admin | With access to the Braintree payment method configuration, one can trigger code execution via PHP object injection. | Magento 2.ane.16, Magento 2.2.7, Magento ii.3.0 |
| PRODSECBUG-2123: PHP Object Injection (POI) and Remote Code Execution (RCE) in the Admin | Via Varnish configuration settings and the design configuration, one can trigger code execution via PHP object injection. | Magento 2.1.16, Magento ii.2.7, Magento 2.3.0 |
| PRODSECBUG-1589: Stops Brute Force Requests via bones RSS authentication | The assailant was able to guess the admin password via brute forcefulness requests to the RSS nodes. | Magento Open Source 1.ix.4.0, Magento Commerce 1.xiv.iv.0 |
| PRODSECBUG-2198: SQL Injection vulnerability through an unauthenticated user | Via an SQL injection vulnerability, i can execute arbitrary code, causing data leakage. | Magento Open Source one.9.iv.one, Magento Commerce 1.14.4.1,Magento 2.1.17, Magento 2.two.8, Magento ii.iii.ane |
| PRODSECBUG-2261: Arbitrary code execution due to dangerous deserialization of a PHP annal | Malicious code tin can exist injected via Phar deserialization vulnerability. | Magento Open Source 1.9.4.1, Magento Commerce 1.fourteen.4.1,Magento two.ane.17, Magento 2.2.viii, Magento 2.three.ane |
| PRODSECBUG-2253: Arbitrary code execution due to dangerous handling of a malicious layout update | An arbitrary PHP code could be executed by one with access to dataflow importer and catalog categories. | Magento Open up Source 1.ix.4.1, Magento Commerce 1.14.4.1 |
| PRODSECBUG-2192: Remote code execution though crafted newsletter and electronic mail templates | The arbitrary code could remotely be executed via crafted newsletter or email template code. | Magento 2.one.17, Magento 2.2.8, Magento 2.3.1 |
| PRODSECBUG-2287: Remote lawmaking execution through electronic mail template | Arbitrary code can be executed via email templates. | Magento 2.1.17, Magento 2.2.8, Magento 2.3.1 |
| PRODSECBUG-2236: SQL Injection and cross-site scripting vulnerability in Itemize section (XSS) | Ane can manipulate attribute_code in the Catalog section and embed malicious code through a stored cross-site scripting vulnerability or an SQL injection vulnerability | Magento 2.1.17, Magento 2.2.8, Magento 2.3.1 |
| PRODSECBUG-2289: Capricious codecould be executed in the admin logging configuration | A user with admin privileges and admission to the advanced admin logging configuration could trigger remote lawmaking execution. | Magento Open Source 1.9.four.two, Magento Commerce 1.14.four.2 |
| PRODSECBUG-2262: Arbitrary code could be executed by importing malicious dataflow profiles | A user with privileges to edit block permission, import dataflow functionality and modify CMS content could execute arbitrary code by importing malicious dataflow profiles. | Magento Open up Source ane.ix.four.2, Magento Commerce 1.14.4.ii |
| PRODSECBUG-2351: Arbitrary code could be executed via crafted sitemap creation | A user with administrator privileges to create sitemaps could execute capricious code by crafted filenames that included php extension inside the XML filename. | Magento Open Source ane.nine.4.2, Magento Commerce i.14.iv.2, Magento 2.i.18, Magento 2.2.9, Magento 2.3.two, SUPEE-11155 |
This is obviously an incomplete list; go to https://magento.com/security you lot can find the full history of Magento security patches.

Partner With Us
Let's discuss how to abound your concern. Get a Complimentary Quote.
Talk to Andrey
Since Magento company realizes how critical information technology is to discover a security vulnerability before hackers do it and use it for illicit purposes, in that location are bounties assigned for detecting and submitting a Magento vulnerability. Find the rewards policy guidelines at https://hackerone.com/magento.
How to install Magento security patches
There are three ways to install Magento patches: via GitHub, manually and with a composer. Below you will find a comprehensive education of how to install Magento patches following these 3 techniques.
Method 1: how to install Magento patch using GitHub
Step #ane: create a directory for patches.
Go to the piece of work directory of the webstore and create a patches directory for storing Magento patches.
Step #two: re-create Magento patches to the created directory.
Employ SSH, FTP-customer and other suitable tools for this step.
Step #3: generate a patch file.
Run the following command git diff > ./patches/patchForModule.patch.
In our case, we make changes in registration.php file of our module. The changes will look the following style:
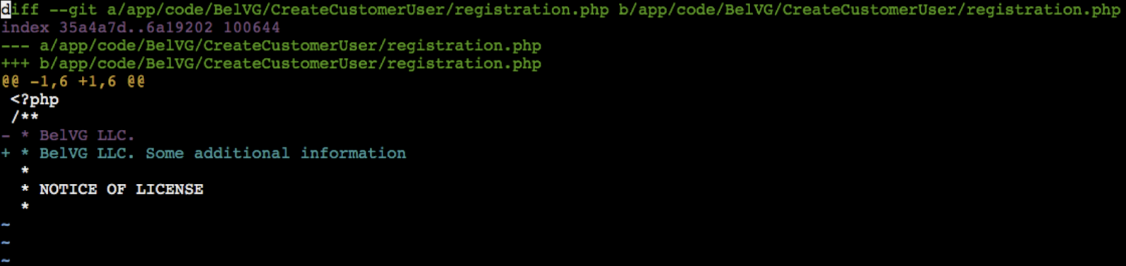
Method two: how to install Magento patch manually
To install a Magento patch via Composer, use git utilise or patch commands.
Connect through SSH and run 1 of the following commands from the root of the website:
git apply patches/patchForModule.patch
or
patch -p1 < patches/patchForModule.patch
Method three: install Magento patch with Composer
Step #1: add a new module via composer for patch application.
For this, run the following command:
composer crave cweagans/composer-patches ~1.0
I will demonstrate this method using JS validation consequence as an instancehttps://github.com/magento/magento2/issues/21734
We tin can fix the outcome using commits.
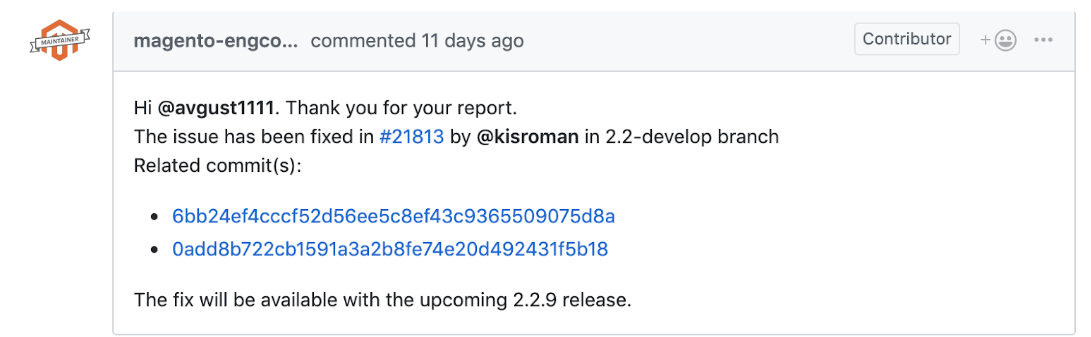
Stride #two: Create two new patch files in the patches directory:
github-issue-21734-magento-ui.unequal
https://github.com/magento/magento2/commit/6bb24ef4cccf52d56ee5c8ef43c9365509075d8a.diff
github-issue-21734-magento-itemize.diff
https://github.com/magento/magento2/commit/0add8b722cb1591a3a2b8fe74e20d492431f5b18.diff
Pace #3: Change the paths in the patches for a root directory of the module to perform the correct update.
Before:
diff –git a/app/code/Magento/Ui/view/base/web/js/lib/validation/rules.js b/app/code/Magento/Ui/view/base/web/js/lib/validation/rules.js
After:
diff –git a/view/base/spider web/js/lib/validation/rules.js b/view/base/web/js/lib/validation/rules.js
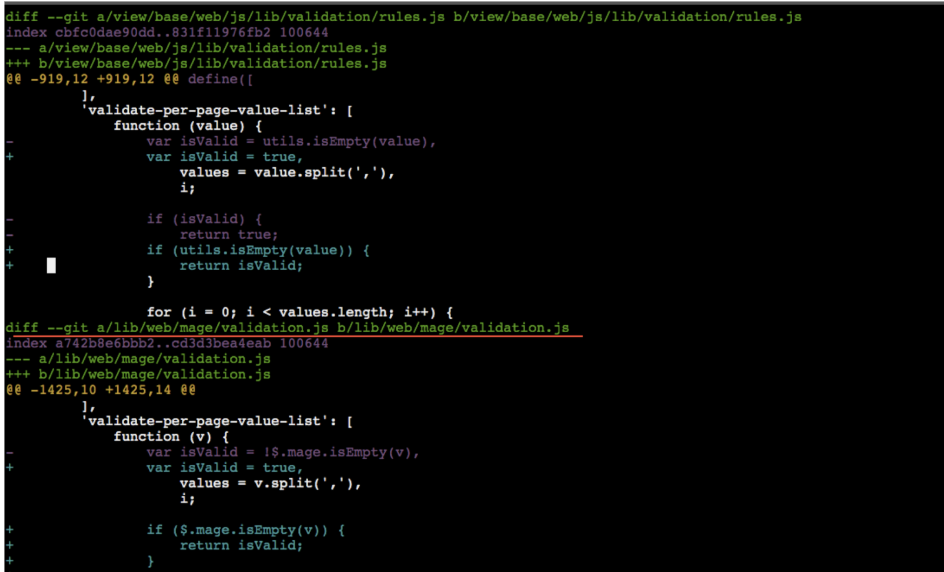
For github-issue-21734-magento-ui.unequal we volition get
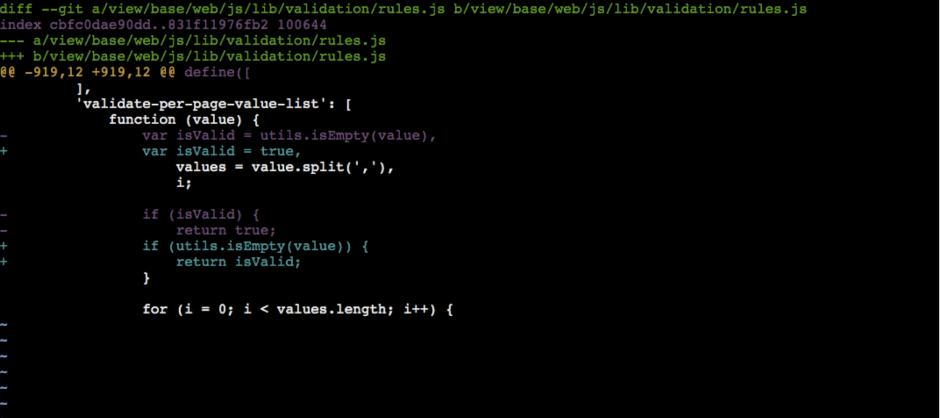
Pace #iv: Change the composer.json file.
Add patches directive to the extra directive.
| "extra" : { "magento-force" : "override" , "patches" : { "magento/module-ui" : { "Patch for issue 21734" : "patches/github-issue-21734-magento-ui.unequal" } , "magento/module-catalog" : { "Patch for upshot 21734" : "patches/github-result-21734-magento-catalog.diff" } } } |
Stride #5: Apply patches and update composer.lock:
Run the post-obit commands:
composer -v install
composer update –lock
How to check Magento shop security
Apart from regularly updating Magento security patches, it is essential to keep a close look at your store security and be able to detect system vulnerability at the early stages. Magento store security cheque tin can be performed direct via the admin panel of the store; in add-on to this, in that location are tertiary-political party tools – Mage Report and Mage Browse – they provide shop security assay without the need to log in to the admin console.
Method ane: How to run a security scan from Magento admin console
Magento Security Browse is a newly introduced tool that allows to monitor your store'southward security, discover unauthorized access and update malware patches.
Step #i: Sign in to Magento account.
Step #2: Choose Security Browse in the panel on the left and press Go to Security Browse button. Tap Agree to go along.
Step #3: Click Add Site at the Monitored Websites field or + Add Site button.
Step #4: Verify your webstore domain buying by inbound Site URL and Site Proper noun at the corresponding field and tap Generate Confirmation Code. Re-create the code to the clipboard.
Step #v: Log in to the store admin panel. Navigate to Content tab -> Design -> Configuration.
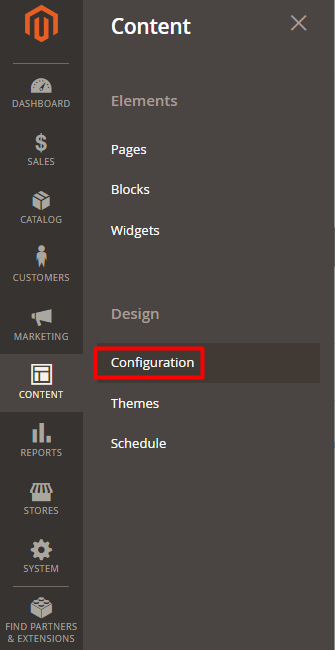
Footstep #6: Expand the HTML Caput section and paste the copied confirmation lawmaking to the Scripts and Mode Sheets field.
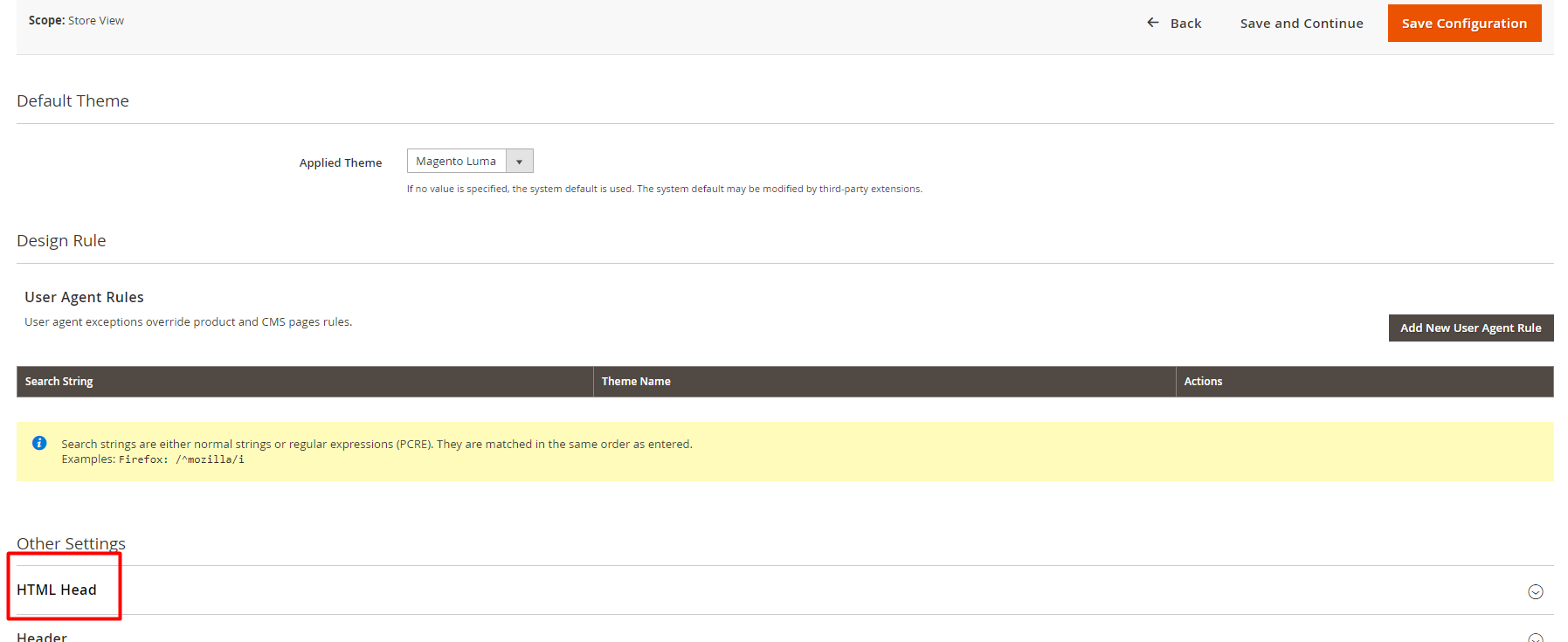
Pace #7: Get back to Security Scan and press Verify Confirmation Lawmaking button.
Stride #8: Configure your security browse to be run either weekly or daily. Press Submit.
Method 2: How to run a security scan with Mage Report
We will run a Magento security scan on a Blaha Gartenmöbel – dwelling & garden webstore BelVG worked with.
Footstep #ane: Go to https://world wide web.magereport.com/

Step #2: Enter the address of the store you wish to check and press Go.

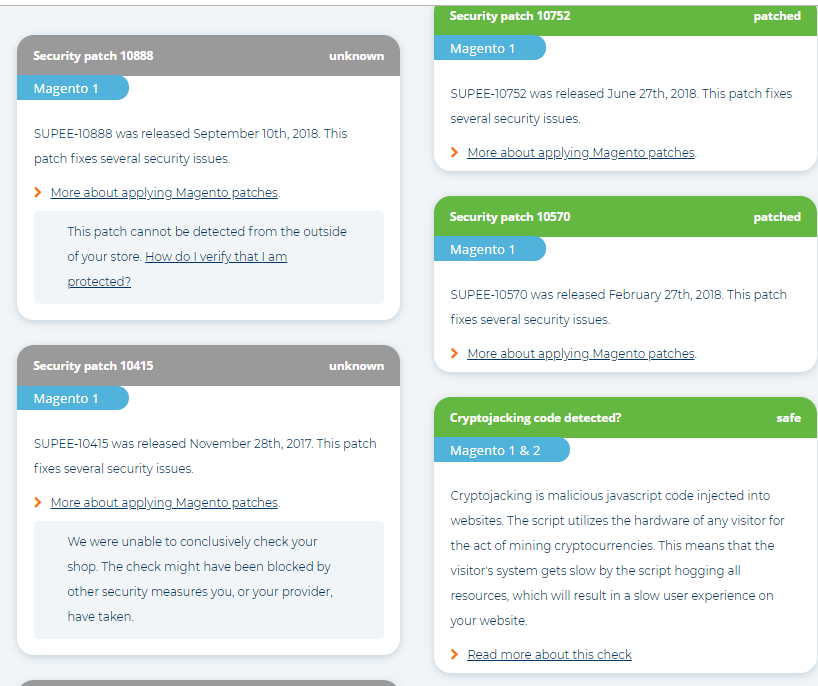
Step #3: Analyze the report you lot got. It consists of the list of patched vulnerabilities (in greenish boxes) and patches with unknown condition (in greyness boxes). Y'all tin acquire more about each security patch; in some cases, there is How exercise I verify that I am protected? link.
Method iii: How to run a security browse with Mage Scan
We will run a Magento security scan on a Karmaloop – manner and shoe webstore BelVG worked with.
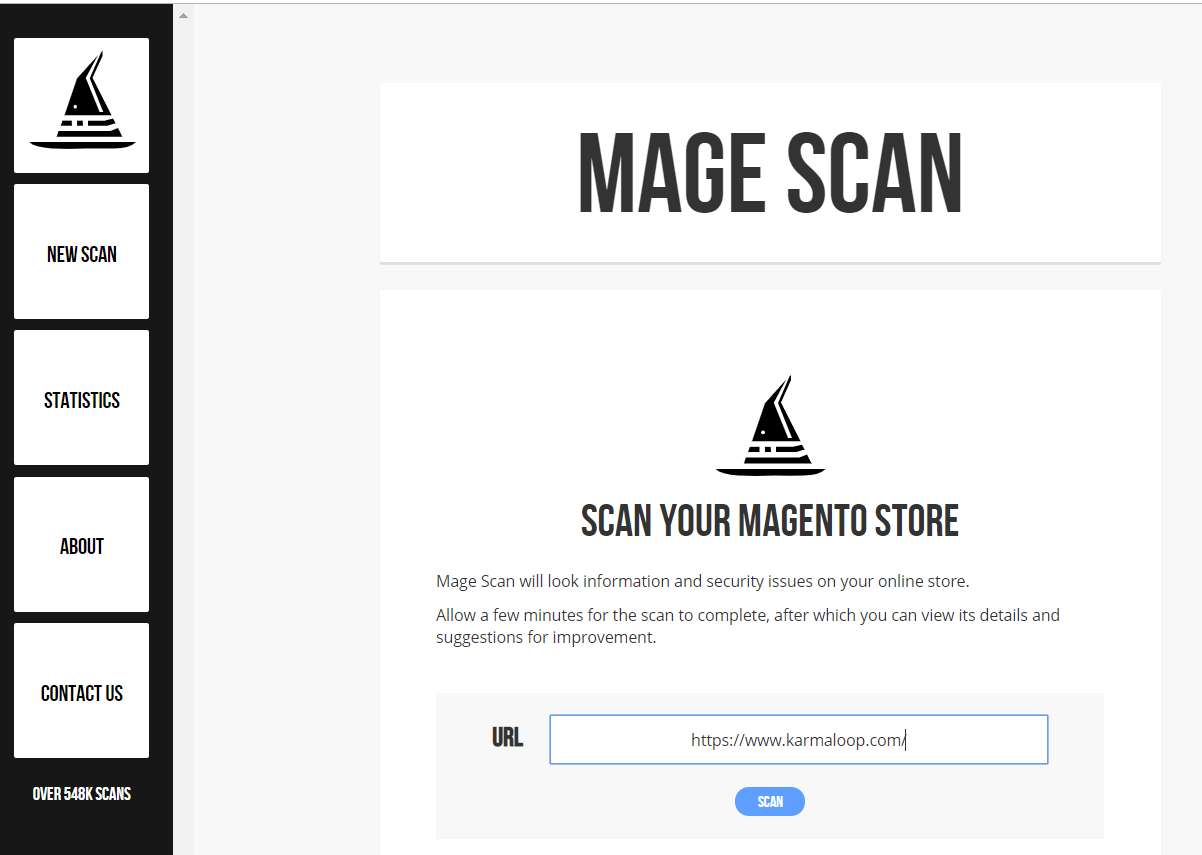
Step #i: Go to https://magescan.com/.
Step #ii: Enter the address of the shop y'all wish to check and press Scan.
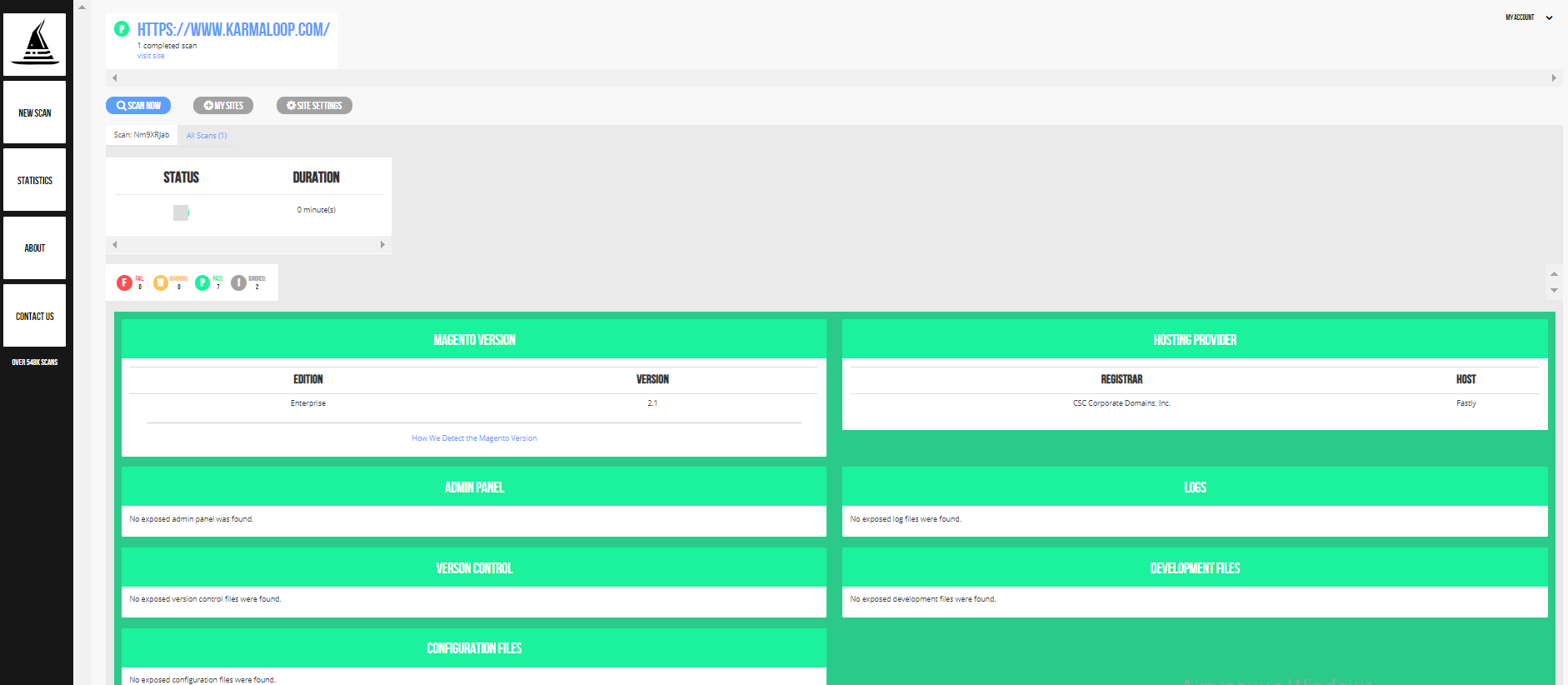
Step #iii: Analyze the report you got. It consists of the following fields: Magento version, hosting provider, admin panel, logs, version control, development files, configuration fields, PHP version and spider web server. If there are no vulnerabilities, each box will comprise the "No exposed configuration files were institute" message.
Wrapping it upwardly
I hope that from my commodity you realized the importance of Magento security patches and learned how to install and update them.
If you are not technically adept enough to piece of work with Magento security patches yourself and you need specialized support, turn to BelVG team for professional person patch installation.
Source: https://belvg.com/blog/how-to-install-magento-2-security-patches.html
Posted by: trevinomostases.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Install Microsoft Security Patches"
Post a Comment